Wannacry
What is the WannaCry ransomware?
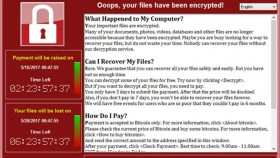
WannaCry searches for and encrypts 176 different file types and appends .WCRY to the end of the file name. It ask users to pay a US$300 ransom in bitcoins. The ransom note indicates that the payment amount will be doubled after three days. If payment is not made after seven days, the encrypted files will be deleted.
Can I recover the encrypted files or should I pay the ransom?
Decryption of encrypted files is not possible at present. If you have backup copies of affected files, you may be able to restore them. Symantec does not recommend paying the ransom.
In some cases, files may be recovered without backups. Files saved on the Desktop, My Documents, or on a removable drive are encrypted and their original copies are wiped. These are not recoverable. Files stored elsewhere on a computer are encrypted and their original copies are simply deleted. This means they could be recovered using an un-delete tool.
When did WannaCry appear and how quickly did it spread?
WannaCry first appeared on Friday, May 12. Symantec saw a dramatic upsurge in the number of attempts to exploit the Windows vulnerabilities used by WannaCry from approximately 8:00 GMT onward. The number of exploit attempts blocked by Symantec dropped slightly on Saturday and Sunday but remained quite high. Exploit numbers increased on Monday, presumably as people returned to work after the weekend.
Who is impacted?
Any unpatched Windows computer is potentially susceptible to WannaCry. Organizations are particularly at risk because of its ability to spread across
networks and a number of organizations globally have been affected, the majority of which are in Europe. However individuals can also be affected.
Is this a targeted attack?
No, this is not believed to be a targeted attack at this time. Ransomware campaigns are typically indiscriminate.
Why is it causing so many problems for organizations?
WannaCry has the ability to spread itself within corporate networks without user interaction, by exploiting known vulnerabilities in Microsoft Windows. Computers that do not have the latest Windows security updates applied are at risk of infection.
How is WannaCry spread?
While WannaCry can spread itself across an organization’s networks by exploiting a vulnerability, the initial means of infection—how the first computer in an organization is infected—remains unconfirmed. Symantec has seen some cases of WannaCry being hosted on malicious websites, but these appear to be copycat attacks, unrelated to the original attacks.
How does the ransom payment work?
The WannaCry attackers request that the ransom be paid using Bitcoins. WannaCry generates a unique Bitcoin wallet address for each infected computer, however due to a race condition bug this code does not execute correctly. WannaCry then defaults to three hard-coded Bitcoin addresses for payment. The attackers are unable to identify which victims have paid using the hard-coded addresses, meaning that victims are unlikely to get their files decrypted.
The Wannacry attackers subsequently released a new version of the malware that corrected this flaw, however this version was not as successful as the original.
Recent Posts
How to Identify and Help Remove an Ice Dam
Sometimes, even your best efforts to prevent an...How to Help Prepare Your Boat for Spring
Are you one of the millions of boaters with spr...Space Heater Safety Tips
In order to save money in the colder months, ma...Umbrella Insurance Coverage
Umbrella insurance provides extra liability cov...5 Tips to Protect Your Possessions with Valuable Items Insurance Coverage
You may think that a homeowners insurance polic...